What is End-to-End Encryption?
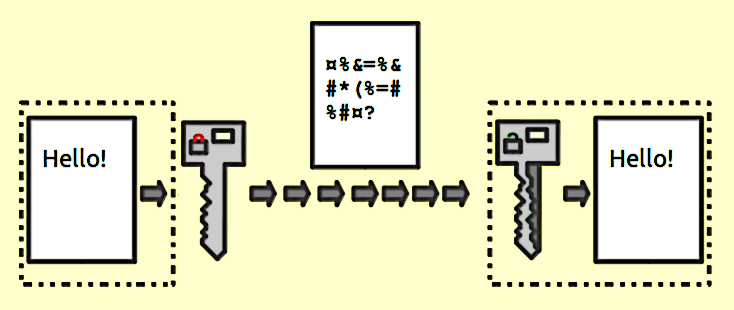
End-to-End encryption, also known as Asymmetric encryption, is a means of encryption that ensures the privacy and security of any data that is being transferred between two ends. It disallows tampering or spying and can be proof of transferring and receiving some content. Secure messaging and data transferring tools like VPNs exist around us. These tools mask any data shared between the sender and recipient, making it look illegible to anyone else. Many platforms have already integrated E2EE into their security protocols, such as WhatsApp and Messenger. When E2EE is absent, service providers can also hold copies of the private decryption keys. Services such as Microsoft and Gmail can then read the data that is being shared. This includes but is not limited to files, location, and direct emails.
How End-to-End Encryption works
Other secure encryption means exist, but they are not without their faults and shortcomings. Single-key encryption, otherwise known as Symmetric encryption, also provides a firm basis for encryption between the sender and recipient. However, it uses only one key to encrypt everything. This makes the data look incomprehensible to any intermediaries relaying the message from sender to recipient.
However, as it is one key, the data can be intercepted, decrypted, and spied on by anyone who knows the key. If any third party gets hold of the key, privacy and security are no longer guaranteed.
What makes E2EE more secure is the existence of two keys, which are divided between the sender and recipient. Those two keys are unique to each endpoint. With two different keys, the challenge of hacking encryption becomes twice as difficult. This method keeps third parties from accessing the key and decrypting the message, as it becomes impossible to hold both keys.
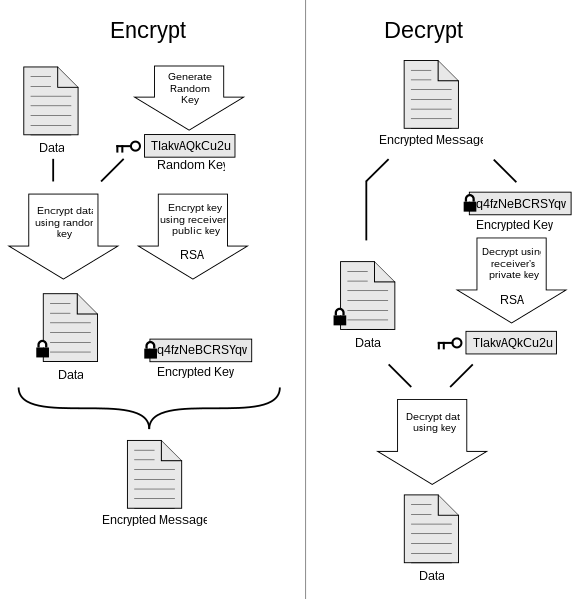
Asymmetric Encryption is important as it safeguards our privacy and security. It provides us with the reassurance that our data is protected from the moment it is sent to the moment it is received by the intended party. This is mainly ensured through the exchange of Public and Private keys, which are formed simultaneously. When we encode a message using our recipient’s public key, they can decode it using the matching private key- which belongs to the sender!
Advantages of End-to-End Encryption
Along with the earlier mentioned benefits, here is a list of some more benefits:
Prevents hacks
Since you are the only carrier of the private decryption key, no one else can take your data! This is because they do not have any key to decrypt the information, and without the key, the information is indecipherable. Also, if you are using a VPN, make sure it does not leak your DNS and IP address. You can use a DNS leak test tool to make sure that your encryption is spot on.
Protects fundamental privacy
Service providers can collect and store data on their servers. If they don’t use E2EE, then not only can the providers see all the data that users upload to their servers, but unwanted third parties, too. This means that users' data is left out for hackers or other agencies to source, collect, or read.
Protects admins
As the encryption and decryption keys are only for the sender and recipient, the admin and service provider won’t be hacked. That is because no data can be sourced from the admin.
Prevents the theft of intellectual or personal data
As all data is safeguarded and protected by encryption, it adds an extra layer of security. This ensures that your data can not be hacked into, thus, guaranteeing your security.
Programs for End-to-End Encryption
The first of two means is Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryptions. It works by ensuring there is a private and a public key, and then it creates an additional single layer of encryption onto the public key. This makes it twice as secure as any single means that uses only a single layer of encryption on either key.
PGP uses encryption and hash algorithms such as DES and MD5 and allows segmentation so that all data can be transferred uniformly. It is extremely helpful in creating secure email messages and ensuring privacy, integrity, and authenticity in communication.
PGP works in a few simples steps:
- The Receiver generates public and private keys when the Sender wants to send an email
- The Receiver sends a copy of the public key to the Sender
- Using the Receiver’s public key, the Sender encodes the contents of the email
- When the email is sent, the Receiver decodes the email with the Sender’s private key
What sets PGP apart from other programs is that the management of keys is solely in the hands of the end-users. The users are wholly responsible for sending their keys to anyone they want to come into communication with. Hence, if one was to lose their device, they would have to exchange public keys with new contacts once more.
Next, we have Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME), which uses digital certificates and signatures to guarantee authenticity. What sets this apart is that no private keys are used. The program allows senders to digitally sign their emails so that only the receiver can receive the message.
One main issue with this program is that it is unavailable for web-based email clients and is inaccessible through any web portals. However, S/MIME is already integrated and ready to use in many mail agents, such as Netscape, MS Outlook, and more.
Further Explanation of Public Keys
Public Key Encryption, also referred to as Asymmetric Encryption, focuses on the engagement between two people. It allows each user of a conversation to create a public and a private key; these keys co-exist and are inherently connected. This connection exists between their code, which presents a challenge to any unwanted third-party hackers or intermediaries.
Using a Public Key, anyone can send any data through an open, unprotected channel. That is because of the fact that the only carriers of both keys are the two participants of the conversation.
Having someone’s public key allows you to encrypt messages to send to them. In the same line of reasoning, your private key allows you to decrypt any messages sent to you. This whole time, intermediaries such as platforms for data transfer will be unable to see the content of the messages.
The only data visible to the service provider will be the metadata: who is sending what content to whom, at what time the message is sent and received, and the subject line of the message, but not the actual content of the message. What will be visible to them, though, is that the message is encrypted.
Through this, when the receiver decrypts a message signed off by the sender, they have the reassurance that it was not tampered with. Public key encryption allows you to confirm identities through various means, all of which add to its security.

